In today's digital age, the average computer user is bombarded with a plethora of applications that they need to access daily. From email, instant messenger, and intranet to various third-party applications, the list of applications seems to be never-ending. Logging into each of these applications every day is not only time-consuming but also requires memorizing numerous login credentials, adding to the frustration of the already overwhelmed user.
This is where Single Sign-On (SSO) comes in as a lifesaver. SSO is a mechanism that allows users to authenticate once and access multiple applications without having to enter their credentials again. With SSO, users can access all their applications using only one login credential, eliminating the need to remember multiple usernames and passwords. This not only simplifies the login process but also saves time and reduces the risk of forgotten passwords and lockouts.
How IT Can Benefit from SSO?
Implementing SSO can also benefit IT administrators and organizations by reducing administrative overhead. Instead of managing individual user accounts and passwords for multiple applications, IT administrators can centralize access control and enforce consistent security policies across applications. This can improve security and simplify the management of user accounts, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
What is SAML?
Single Sign-On (SSO) has been used for many years in digital environments, where users authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications. However, the implementation of SSO for web-based applications has been challenging. In the absence of a standard protocol for SSO in web-based applications, each vendor developed its own proprietary solution. This made it difficult for users to authenticate and gain access to multiple applications from different vendors.
To address this challenge, an XML-based open standard format called Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) was developed.
SAML is a widely adopted protocol used for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, specifically between:
- An identity provider (IdP) and,
- A service provider (SP).
With SAML, system administrators can engage third-party identity providers that can grant users access to multiple systems and applications. The user authenticates with the identity provider, and the identity provider generates a SAML assertion containing information about the user's identity and attributes.
The SAML assertion is then sent to the service provider, which verifies the signature and attributes in the assertion. If the service provider trusts the identity provider and the attributes in the assertion are sufficient for authentication, the user is granted access to the application.
SAML has become the de facto standard for SSO in web-based applications because:
- It has the most modern identity.
- It has access management systems support within it.
- It is a flexible and secure protocol that enables users to access multiple applications using a single set of credentials.
By leveraging SAML, organizations can simplify the login process, reduce the risk of forgotten passwords and lockouts, and improve security and productivity.
SAML Components
SAML is composed of several components, including:
1. Identity Provider (IdP)
The IdP is responsible for authenticating users and generating SAML assertions. The IdP acts as a centralized authentication service and manages user identities and credentials.
2. Service Provider (SP)
The SP is responsible for protecting resources and applications. The SP trusts the IdP and relies on SAML assertions to authenticate users.
3. SAML Assertion
A SAML assertion is an XML document that contains information about a user's identity and attributes. The assertion is digitally signed by the IdP to ensure its authenticity.
4. SAML Protocol
The SAML protocol defines a set of messages and interactions between the IdP and SP. The protocol specifies how SAML assertions are exchanged and verified.
How Does SAML Work?
SAML is a powerful protocol that enables organizations to achieve SSO for web-based applications. To understand how SAML works, let's consider an example scenario:
1. A user attempts to access a service from a service provider (SP) by sending a request through a user agent (such as a browser).
2. The service provider redirects the user to an identity provider (IdP) for authentication.
3. The identity provider challenges the user for their credentials, such as a username and password.
4. Once the user's credentials are verified, the identity provider creates a SAML assertion containing information about the user's identity, attributes, and authentication status. The assertion is digitally signed using the identity provider's private key to ensure its authenticity and integrity.
5. The identity provider sends the SAML assertion back to the service provider.
6. The service provider verifies the SAML assertion's signature to ensure that it came from the trusted identity provider.
7. The service provider extracts the user's identity and attributes from the SAML assertion and authorizes the user's access to the requested service.
8. The user is granted access to the service.
This process happens behind the scenes and is transparent to the user. The user only needs to authenticate once with the identity provider, and from then on, can access any service provider that trusts the identity provider.
SAML enables the secure exchange of user authentication and authorization data between web domains. By creating a common framework for transmitting SAML assertions among identity providers and service providers, it does this. The user's identity, characteristics, and any security-related information, such as the session length and authentication status, are all included in SAML assertions.
SharePoint SSO Using ADFS With SAML
SharePoint is an essential tool for many organizations, allowing teams to collaborate on projects, store documents, and share information. However, logging in to SharePoint every time you need to access it can be tedious and time-consuming, especially when you have to remember multiple sets of login credentials for different applications.
That's where SharePoint Single Sign-On (SSO) using ADFS with SAML comes in. This authentication setup simplifies two things at a time:
- First making the login process easy
- Second, allowing users to access SharePoint resources using only one set of credentials.
Here's How it Works:
- Step 1: When a user wants to access a SharePoint resource, the SharePoint web application sends an authentication request to ADFS, prompting the user to enter their username and password.
- Step 2: ADFS, which stores user information like login ID, name, and email address, authenticates the user and generates a SAML XML message that includes a SAML assertion, which contains information about the user's identity and authentication status.
- Step 3: This SAML message is then sent back to the SharePoint web application, which validates it to ensure that it was signed by the ADFS server and that it is still valid.
- Step 4: Once the assertion is validated, the SharePoint web application grants the user access to the requested resource.
This process simplifies authentication for users, as they only need to enter their login credentials once to gain access to multiple SharePoint resources. It also increases security by centralizing user authentication and reducing the need for users to manage multiple sets of login credentials.
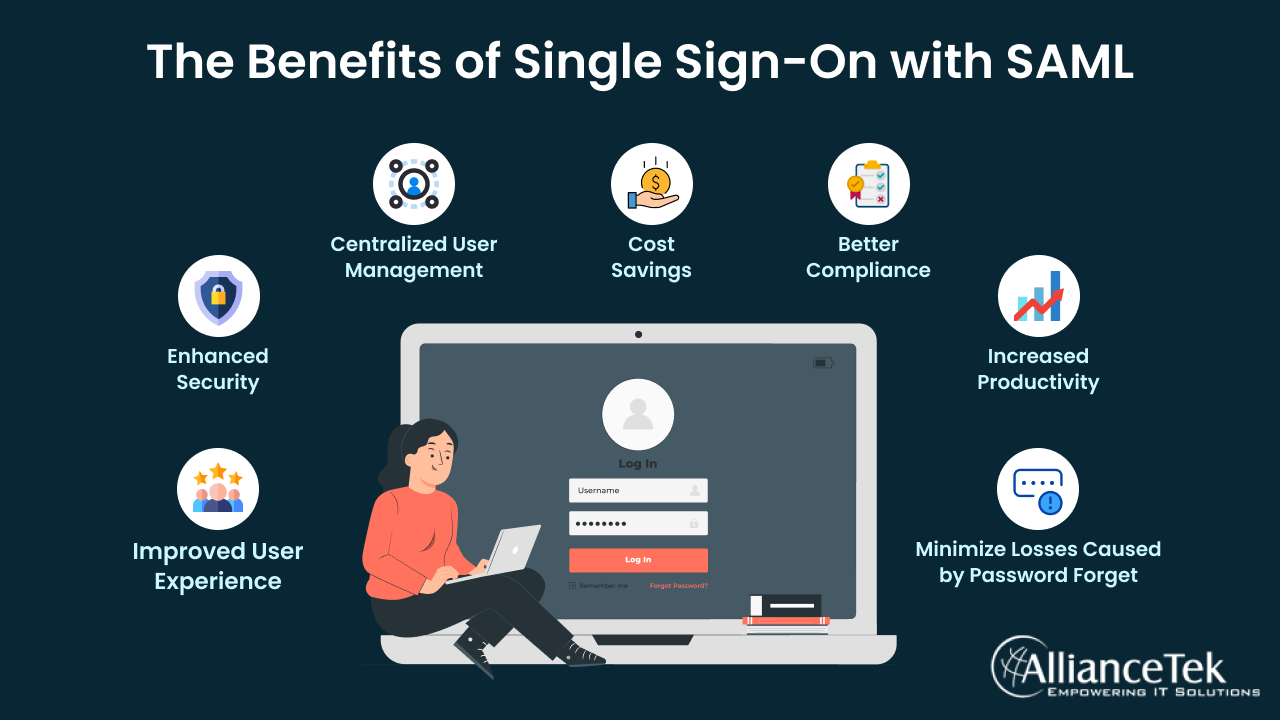
Benefits of SSO Using SAML
Single Sign-On (SSO) using Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) offers several benefits for users and organizations, including
1.Improved User Experience
SSO using SAML eliminates the need for users to remember multiple sets of login credentials for different applications. They only need to enter their credentials once to access all the applications connected to the SSO system.
2. Enhanced Security
SAML provides a secure method of exchanging authentication and authorization data between service providers and identity providers. It uses cryptographic techniques to ensure that only authorized parties can access user information.
3. Centralized User Management
SSO using SAML allows organizations to manage user access from a central location, reducing the burden on IT teams and ensuring that users have access to the resources they need.
4. Cost Savings
SSO using SAML reduces the need for organizations to purchase and manage multiple authentication systems, saving time and money.
5. Better Compliance
Many industries require organizations to adhere to strict security and compliance regulations. SSO using SAML provides an auditable trail of user activity, making it easier for organizations to demonstrate compliance with these regulations.
6. Increased Productivity
SSO using SAML can increase productivity as it reduces the time spent logging into multiple applications and the frustration of having to remember multiple sets of credentials. This can also lead to increased user adoption of applications, as users are more likely to use applications that are easy to access and use.
7. Minimize losses caused by password forget
Another benefit of SSO with SAML is that it reduces the chances of losing passwords, which can be a common problem in organizations. Since users only need to remember one set of credentials, there is less of a chance of forgetting or misplacing them. This reduces the burden on IT help desks, which saves time and money.
SSO using SAML offers significant benefits for both users and organizations. Let's learn some cases to understand briefly.
Common SSO Use Cases for SAML
SAML is widely used for enabling Single Sign-On (SSO) across a variety of use cases. Here are some common SSO use cases for SAML:
1. Enterprise SSO
Large organizations often use SAML to enable SSO across multiple internal applications and systems, such as email, intranet, HR systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools. This helps to simplify authentication for employees and improve productivity.
2. Cloud-based SSO
SAML is commonly used to enable SSO across cloud-based applications, such as Salesforce, Office 365, Google Apps, and Dropbox. This helps to reduce the number of passwords users have to remember, simplify access, and improve security by centralizing authentication.
3. Mobile SSO
SAML can be used to enable SSO for mobile apps, allowing users to access multiple apps using a single set of credentials. This can improve the user experience and reduce the need for users to enter login credentials repeatedly.
4. Partner SSO
SAML can also be used to enable SSO across partner organizations, allowing employees of one organization to access resources or applications of another organization without the need for separate authentication. This can improve collaboration and streamline business processes.
5. Federated SSO
SAML is commonly used for federated SSO, where multiple organizations agree to share authentication information in a trusted way. This enables users to access resources across multiple organizations without having to re-enter login credentials. Federated SSO is often used in research and education communities, where users need to access resources across multiple institutions.
Hence, SAML is a versatile protocol that can be used to enable SSO across a variety of use cases, improving security, productivity, and user experience.
Call us at 484-892-5713 or Contact Us today to know more details about the benefits of single sign-on with SAML.


